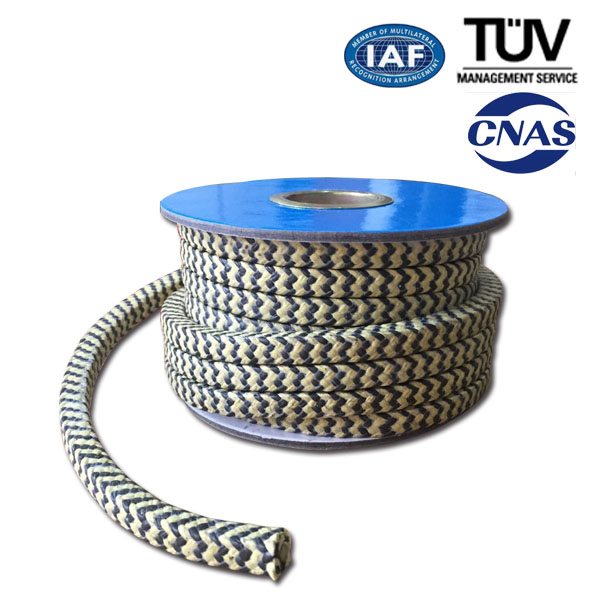
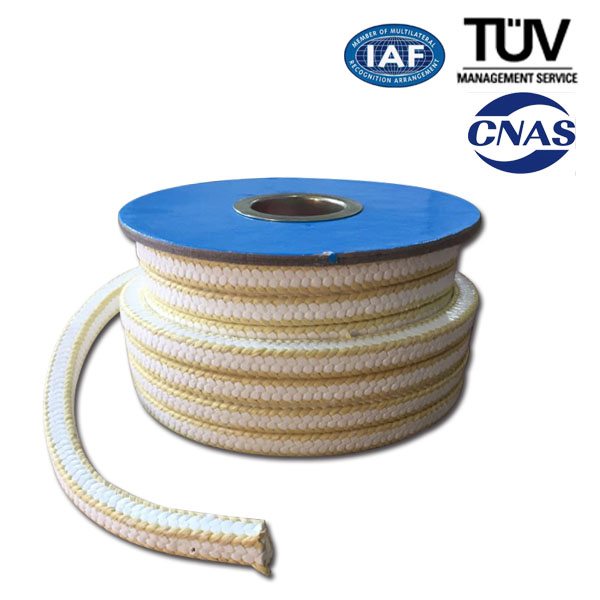
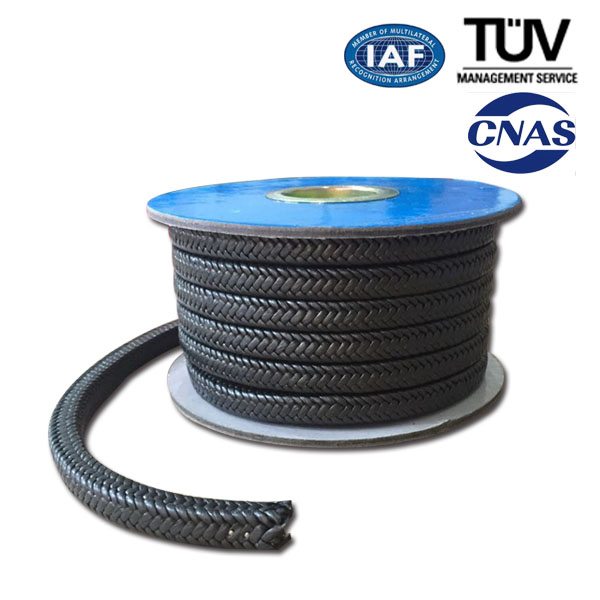
High Efficiency Factory PTFE Graphite Braided Packing for Kyrgyzstan Factory
High Efficiency Factory PTFE Graphite Braided Packing for Kyrgyzstan Factory Detail:
It is a braided packing made of PTFE yarn containing graphite. It is recommended for shafts for almost all chemicals. Stability and long service lift are achieved by low friction coefficient. It has great tear strength and high thermal conductivity. This self lubrication packing does not score the shaft and minimizes sleeve rep, acement cost. It can be used to seal alkalis, solvents, water, steam, acids except strong oxidizing acids( aqua regia, fuming nitric acid, fuming nitric acid, fuming sulfuric acid,etc.) for centrifugal pumps, autoclaes, agitators mixers, etc.
Technical Data Sheet
|
|
Rotating |
Reciprocating |
Valves |
|
Pressure |
2Mpa |
15Mpa |
15Mpa |
|
Shaft Speed |
14m/s rotary |
||
|
Temperature |
-200℃~+280℃ |
||
|
PH Range |
0~14 |
||
Application Area
It can be used to seal alkalis, solvents, water, steam, for centrifugal pumps, autoclaves, agitators, mixers, etc.
Product detail pictures:

Related Product Guide:
Comparison of O-Ring Materials
O-Ring Sizes for Industrial Applications
High Efficiency Factory PTFE Graphite Braided Packing for Kyrgyzstan Factory, The product will supply to all over the world, such as: , , ,
Spark Gap RU-69 for aviation engine ignition systems sales@dmphotonics.com
Triggered Spark Gaps sales@dmphotonics.com
https://www.dmphotonics.com/Plasma/Triggered%20Spark%20Gap%20Switches.htm
The first blasting cap or detonator was demonstrated in 1745, when a Dr. Watson of the Royal Society showed that the electric spark of a Leyden jar could ignite black powder.
In 1750, Benjamin Franklin in Philadelphia made a commercial blasting cap consisting of a paper tube full of black powder, with wires leading in both sides and wadding sealing up the ends. The two wires came close but did not touch, so a large electric spark discharge between the two wires would fire the cap.
In 1822 the first hot wire detonator was produced by Dr Robert Hare. Using one strand separated out of a multistrand wire as the hot bridgewire, this blasting cap ignited a pyrotechnic mixture (believed to be potassium chlorate/arsenic/sulphur) and then a charge of tamped black powder.
In 1863 Alfred Nobel introduced the first pyrotechnic fuse blasting cap, using mercury fulminate to detonate nitroglycerin.
In 1868, H. Julius Smith introduced a cap that combined a spark gap ignitor and mercury fulminate, the first electric cap able to detonate dynamite.
A detonator is a device used to trigger an explosive device. Detonators can be chemically, mechanically, or electrically initiated, the latter two being the most common.
The commercial use of explosives uses electrical detonators or the capped fuse which is a length of safety fuse to which an ordinary detonator has been crimped. Many detonators’ primary explosive is a material called ASA compound. This compound is formed from lead azide, lead styphnate and aluminium and is pressed into place above the base charge, usually TNT or tetryl in military detonators and PETN in commercial detonators.
Other materials such as DDNP (diazo dinitro phenol) are also used as the primary charge to reduce the amount of lead emitted into the atmosphere by mining and quarrying operations. Old detonators used mercury fulminate as the primary, and it was often mixed with potassium chlorate to yield better performance.
Electrical detonators[edit source
There are three categories of electrical detonators: instantaneous electrical detonators (IED), short period delay detonators (SPD) and long period delay detonators (LPD). SPDs are measured in milliseconds and LPDs are measured in seconds.
In situations where nanosecond accuracy is required, specifically in the implosion charges in nuclear weapons, exploding-bridgewire detonators are employed. The initial shock wave is created by vaporizing a length of a thin wire by an electric discharge.
A new development is a slapper detonator, which uses thin plates accelerated by an electrically exploded wire or foil to deliver the initial shock. It is in use in some modern weapon systems. A variant of this concept is used in mining operations, when the foil is exploded by a laser pulse delivered to the foil by optical fiber.
Electric detonators
Magnetic couplings
Blasting cap
Dead man’s trigger
Detonation
Detonating cord
Detonator (railway)
Exploding-bridgewire detonator
Explosive booster
Explosive material
Firing pin
Fuse (explosives)
NASA standard detonator
Nuclear weapon design
Pencil detonator
Shock tube detonator
Slapper detonator
Triggering sequence
Urchin (detonator)
triggered spark gap ratings
electrostatic analysis of triggered spark gaps
perkin elmer spark gaps
arcing in air
spark gap tube
jacobs ladder high voltage
purpose of spark gap
spark gap voltage
BAE Systems
Battelle Memorial Institute
Czech Technical University
Eglin AFB
Florida A&M University
Johns Hopkins University, Applied Physics Laboratory
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory
Loughborough University
NASA Marshall Space Flight Center
Sandia National Laboratories
Science University of Tokyo
University of Bologna (Italy)
University of California
University of Ferrara (Italy)
Manchester University
University of Southern California
University of Western Australia
US Army Research Laboratory
US Naval Research Laboratory